What Is MFM Meter? Working, Features, Specifications & Applications
In the modern electrical world, monitoring power quality and consumption is essential for safe and efficient operations. Whether in industries, commercial buildings, or residential smart systems, accurate measurement of electrical parameters has become a necessity. This is where MFM meters come into play. If you are wondering “What Is MFM Meter?”, how it works, what features it offers, and where it is widely used—this article explains everything in a clear and beginner-friendly manner.
What Is MFM Meter?
A Multifunction Meter (MFM Meter) is an advanced digital measuring device used to monitor multiple electrical parameters in a single unit. Instead of installing separate voltmeters, ammeters, frequency meters, and power meters, an MFM meter provides all these measurements in one compact device.
It measures:
- Voltage (Phase & Line)
- Current (R/Y/B or any phase)
- Active Power (kW)
- Reactive Power (kVAR)
- Apparent Power (kVA)
- Energy (kWh, kVAh, kVARh)
- Power Factor (PF)
- Frequency (Hz)
- Demand parameters
- Harmonics (on advanced models)
Because of its accuracy and real-time monitoring, the MFM meter has become an essential device in industries, automation systems, control panels, and energy management systems (EMS).
Understanding the Working Principle of an MFM Meter
To understand What Is MFM Meter, it’s important to know how it works.
MFM meters operate on digital signal processing (DSP) and microcontroller-based technology. Here is a simple explanation:
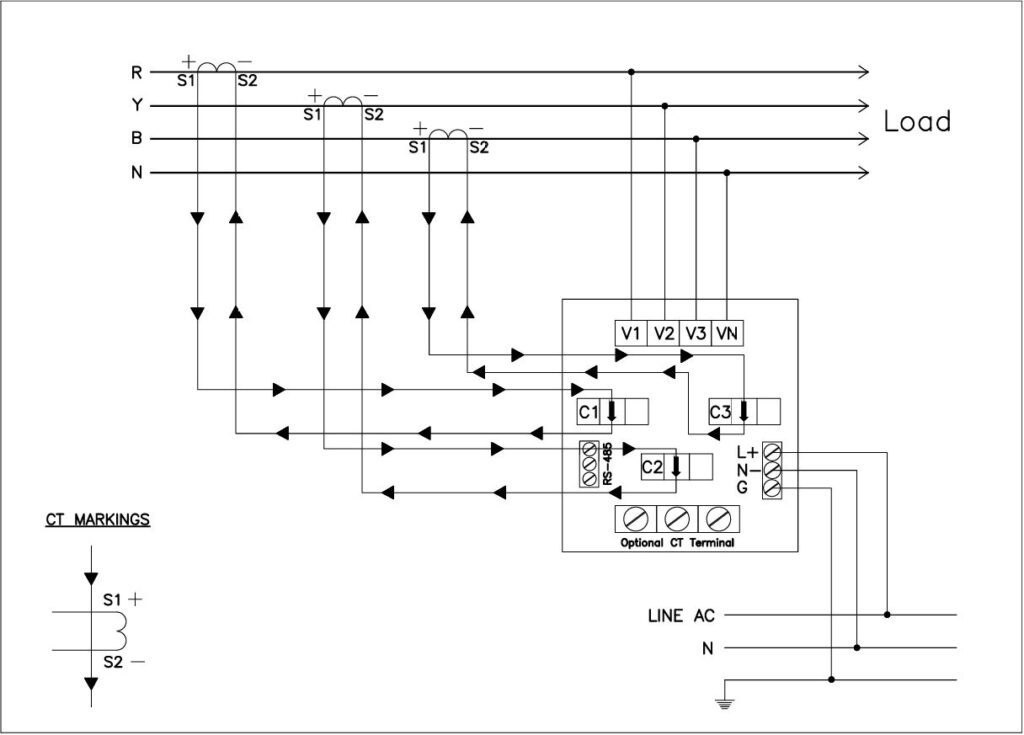
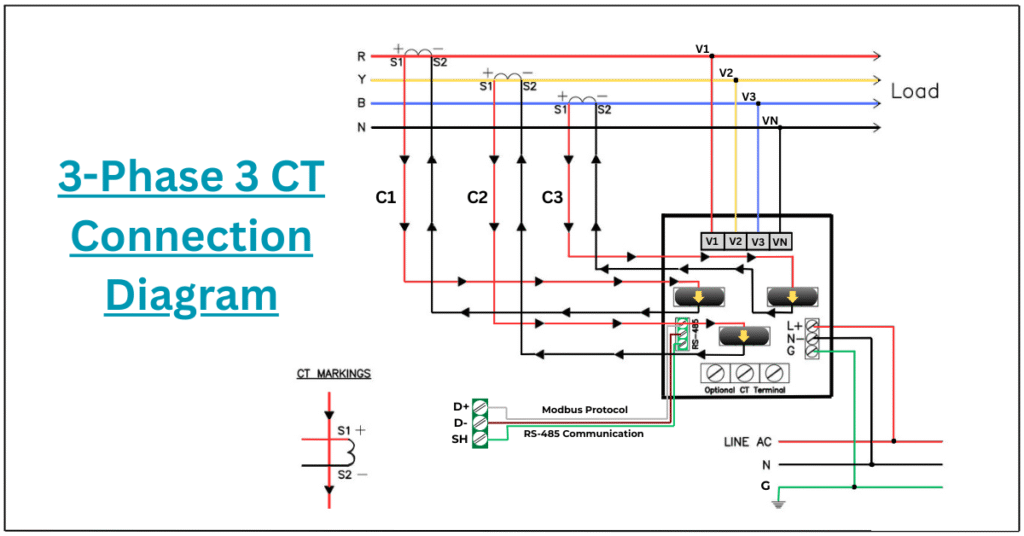
1. Inputs to the Meter
- Voltage is fed directly to the meter.
- Current is fed through CT (Current Transformer).
- In HT systems, PT (Potential Transformer) is used to reduce voltage.
2. Signal Conversion
The voltage and current signals are analog in nature. The meter uses ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converters) to convert these signals into digital form.
3. Parameter Calculation
An internal microcontroller calculates electrical parameters using mathematical algorithms such as:
- RMS calculation
- Vector mathematics
- Power factor angle calculations
4. Real-Time Display
The processed values are shown on an LCD/LED screen.
5. Data Transmission (Optional)
Many MFM meters support communication protocols such as:
- RS485 (Modbus RTU)
- BACnet
- CANbus
- Ethernet (for IoT models)
These allow integration with:
- SCADA systems
- PLCs
- Energy monitoring dashboards
- Cloud-based IoT platforms
Thus, an MFM meter continuously monitors, calculates, and communicates multiple electrical parameters.
Key Features of an MFM Meter
Modern MFM meters come with a wide range of features. Some standard and advanced ones include:
1. Multi-Parameter Monitoring
One of the biggest advantages is that a single meter replaces multiple instruments, saving panel space and cost.
2. High Accuracy Class
Most meters offer:
- Class 1
- Class 0.5S (for energy audits)
- Class 0.2S (for precision industrial applications)
3. Programmable CT/PT Ratio
Suitable for both LT and HT applications. This feature allows:
- Correct scaling of measurements
- Flexible use across various systems
4. RS485 Modbus Communication
Enables:
- Remote monitoring
- Data logging
- SCADA integration
This is particularly helpful in automation and energy management systems.
5. Load & Demand Monitoring
Advanced MFMs provide:
- Maximum demand (MD)
- Demand forecasting
- Load profile recording
6. THD (Total Harmonic Distortion) Measurement
Useful in:
- VFD-heavy systems
- Data centers
- Harmonic analysis
7. Alarm & Event Logging
Meters can generate alarms for:
- Overvoltage
- Undervoltage
- Overcurrent
- Phase reversal
- Neutral loss
8. Compact Size
Panel designers prefer MFM meters because they fit easily into:
- 96×96 mm
- 72×72 mm
standard cutouts.
Technical Specifications of an MFM Meter
While specifications vary by brand (Satec, Schneider, Selec, etc.), here are typical values:
1. Input Voltage
- 57.7/100V (PT Secondary)
- 230/415V (Direct Input)
2. Input Current
- 1A / 5A from CT Secondary
3. Frequency
- Range: 45–65 Hz
4. Measurement Parameters
- kW, kVA, kVAR
- kWh, kVAh, kVARh
- PF, THD
- VLL, VLN, Currents
5. Accuracy
- Voltage: ±0.5%
- Current: ±0.5%
- Power: ±1%
- Energy: Class 1 or 0.5S
6. Communication
- RS485 Modbus RTU
- Optional: Ethernet, Wi-Fi, GSM gateways
7. Display
- Backlit LCD / LED
- 3-row or 4-row multi-line display
8. Power Supply
- 85–270V AC/DC (Universal Power Supply)
Applications of MFM Meters
After understanding What Is MFM Meter, let’s explore where it is commonly used.
1. Industrial Control Panels
MFM meters are widely used in:
- MCC (Motor Control Centers)
- PCC (Power Control Centers)
- APFC panels
- Automation panels
2. Commercial Buildings
Used in:
- Hospitals
- Shopping malls
- Office complexes
- Educational institutions
They help monitor load, power factor, and energy consumption.
3. Utility & Power Distribution
Used in:
- Substations
- DG synchronization
- Transformer monitoring
- HT/LT feeders
4. Renewable Energy Systems
Found in:
- Solar power plants
- Wind energy farms
- Hybrid renewable systems
MFM meters help track generation and load patterns.
5. SCADA & EMS Systems
Used for centralized monitoring and automated data collection.
6. Energy Auditing
High-accuracy MFM meters are used by:
- Energy consultants
- Auditors
- Facility managers
to identify wastage and optimize consumption.
Real-World Example: How MFM Meter Helps in a Factory
Imagine a manufacturing plant with the following issues:
- High electricity bill
- Poor power factor
- Unexpected equipment failures
After installing an MFM meter at the main incoming panel, the facility team observed:
- Excess reactive power (low PF around 0.78)
- High THD due to multiple VFD drives
- Phase imbalance during peak hours
Using this data, they added:
- Capacitor bank for PF improvement
- Harmonic filters
- Balanced the loads
Within 2 months:
- The monthly energy bill reduced
- Machine downtimes decreased
- System became more efficient
This shows how an MFM meter can help in decision-making and energy savings.
Advantages of Using an MFM Meter
✔ Saves cost by replacing multiple meters
✔ Reduces wiring complexity
✔ Provides real-time electrical parameter visibility
✔ Helps in predictive maintenance
✔ Supports energy-saving decisions
✔ Easy integration with SCADA/PLC systems
Limitations of an MFM Meter
✘ Not suitable for revenue billing
✘ Cannot measure extremely high harmonics (in basic models)
✘ Requires proper CT/PT configuration
✘ Needs trained personnel for installation and setup
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Is MFM Meter?
An MFM meter, or Multifunction Meter, is a digital device that measures multiple electrical parameters such as voltage, current, energy, power, PF, and more in a single instrument.
2. Can MFM meters be used for billing?
Generally, no. Billing requires revenue-grade meters with Class 0.2S accuracy.
3. Do all MFM meters support Modbus?
Most modern MFMs support RS485 Modbus RTU, but always check the model specifications.
4. Where should an MFM meter be installed?
It can be installed at:
- Main incomer
- Sub-feeders
- DG panels
- Solar inverters
- MCC/PCC panels
5. What is the typical CT ratio used in MFM meters?
Common CT ratios include:
- 100/5
- 200/5
- 400/5
- 800/5
- 1000/5
The ratio depends on the system load.
6. Is MFM meter suitable for HT applications?
Yes, with proper PT ratio configuration (e.g., 11kV/110V PT).
Conclusion
Understanding What Is MFM Meter is essential for anyone involved in electrical systems, automation, maintenance, or energy management. These meters offer accuracy, versatility, and real-time monitoring capabilities that help industries reduce energy consumption, detect faults, and improve overall system efficiency. With features like Modbus communication, multi-parameter measurement, and advanced data analysis, MFM meters are becoming a standard component in modern electrical installations.
If you manage power systems or design panels, investing in a good-quality MFM meter can significantly enhance your monitoring and decision-making capability.